| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- Node.js
- 알고리즘
- dp
- 플로이드와샬
- Algorithm
- Stack
- Greedy
- sigmoid
- 탐색
- 풀이
- mysql
- 캡스톤정리
- ios
- C++
- 부르트포스
- 그리디
- 문제풀이
- 백준
- Swift
- 백트래킹
- 그래프
- Docker
- DeepLearning
- 프로그래머스
- ReLU
- dfs
- BFS
- NeuralNetwork
- 실버쥐
- Blockchain
- Today
- Total
개발아 담하자
[Deep Learning] Back Propagation 구현하기 본문
Gradient Descent 를 이용해서 Back Prorpagtion 을 구현해보자.
Gradient Descent 란 ? https://silver-g-0114.tistory.com/69
[Deep Learning] Gradient Descent 란 ?
Gradient Descent (경사 하강법) 이란? 일단 w, b 를 임의로 설정한 일차함수와 데이터 사이의 평균 제곱 오차 (MSE : Mean Squared Error) 를 구한다. 이 평균 제곱 오차를 비용 함수(cost function) 이라고 부른..
silver-g-0114.tistory.com
1. functions.py
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-1))
def softmax(x):
e = np.exp(x-np.max(x, axis=1, keepdims=True))
return e / np.sum(e, axis=1, keepdims=True)
def mean_squared_error(y,t):
return np.mean((y-t)**2)
def cross_entropy_error(y,t):
return -np.sum(t * np.log(y + 1e-9)) / y.shape[0]저번에 실습했던 내용과 동일하다.
sigmoid 는 가중치를 전달할 때 부드럽게 양을 조절해 전달하고,
softmax 는 주로 마지막 층에서 사용한다.
mean_squared_error, cross_entropy error 는 지금 예측이 얼마나 좋은지 측정한다.
2. layers.py
2-1. Dense Layer
class Dense:
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, initializer='random'):
self.W = 0.1 * np.random.randn(input_size, output_size)
self.b = 0.1 * np.zeros(output_size)
self.x = None
self.y = None
self.dW = None # W gradient
self.db = None # b gradient
def forward(self, x):
self.x = x # x값을 기억해 둠 (gradient 를 구할 때 사용)
self.y = np.dot(self.x, self.W) + self.b
return self.y
def backward(self, d_out, learning_rate):
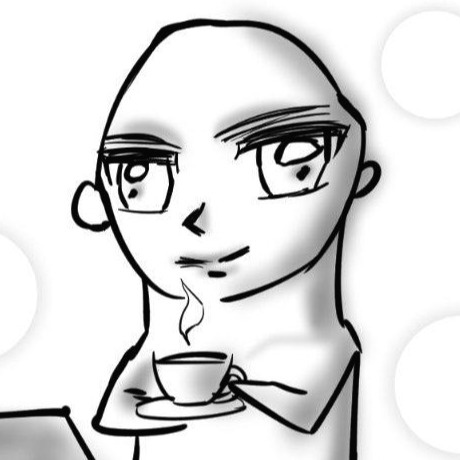
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, d_out)
self.db = np.sum(d_out, axis=0)
d_x = np.dot(d_out, self.W.T)
self.W -= learning_rate * self.dW
self.b -= learning_rate * self.db
return d_x일반 layer 구조이다. 저번 foward pass 에서 backward 가 추가되었다.
dw 는 w 의 편미분 값이고, db 는 b 의 편미분 값이다. d_out 은 global gradinet 값이다.
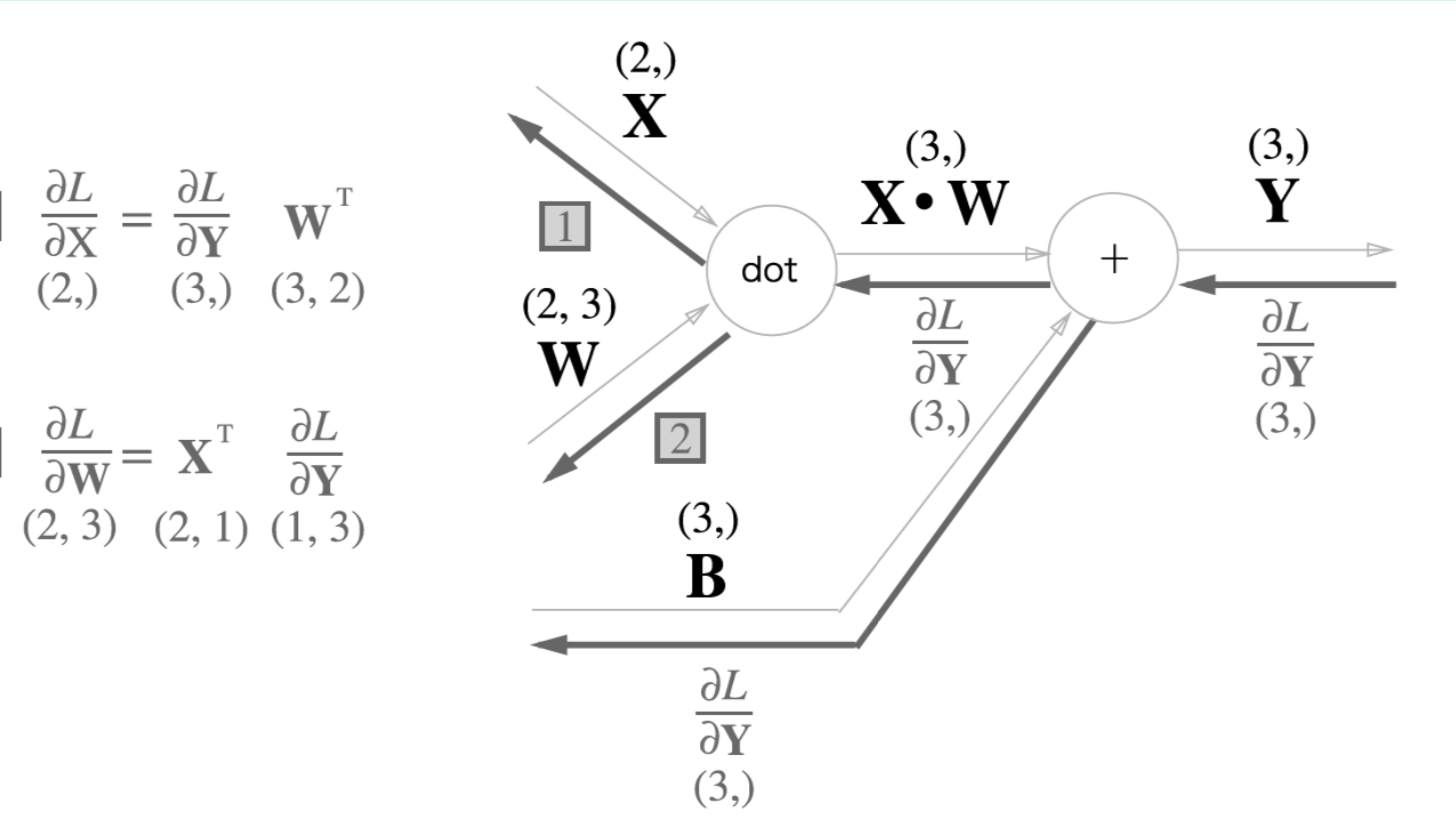
위와 마찬가지로 backward 할 때 d_x 값에 d_out 과 W 의 transpose 값을 곱해준다.
w = w + (-grad) * learning_rate그리고 위의 gradient descent 수식과 마찬가지로 learning_rate 를 곱한 값을 빼준다.
2-2. Softmax Layer
# last layer
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.error = None
self.y = None # 예측 답안
self.t = None # 모범 답안
def forward(self,x):
self.y = softmax(x)
return self.y
def loss(self, t):
self.t = t
self.error = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.error
def backward(self, d_out=1, learning_rate=None):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
d_x = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
return d_x마지막 층에서 사용될 soft max layer 이다.
저번 forward pass 에서 loss 와 backward 가 추가되었다.
softmax function 은 loss 계산으로 cross entropy error 을 사용한다. loss 는 제일 마지막 한 번만 계산한다.
batch_size 는 한 번에 처리할 양을 의미한다.
2-3. Softmax Activation Function
class Sigmoid:
def __init__(self):
self.y = None
def forward(self,x):
self.y = sigmoid(x)
return self.y
def backward(self, d_out, learning_rate=None):
return d_out * (1.0 - self.y) * self.ysigmoid 는 dense layer 의 activation function 으로 쓰인다.
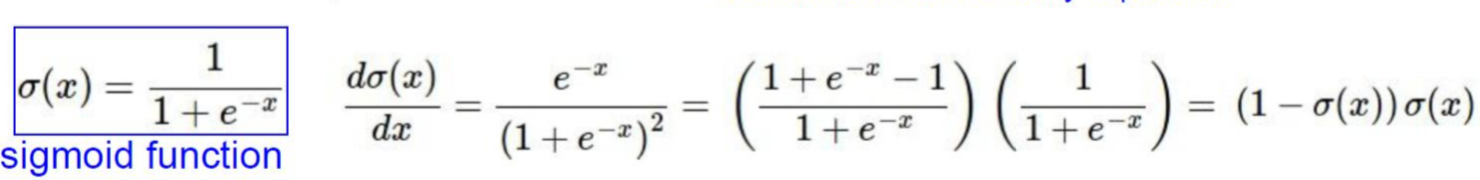
위 식과 마찬가지로 미분 값을 backward 할 때 return 해준다.
2-4. ReLU Activation Function
class Relu:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x<=0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, d_out, learning_rate=None):
d_out[self.mask] = 0
d_x = d_out
return d_xRelu layer는 backward 할 때 x 가 0 이하인 값은 모두 0으로 처리한다.
이제 이렇게 구성된 layer 을 바탕으로 network를 만들고, back propagation 실습을 진행해보자 ❗️
3. Network class
class Network1:
def __init__(self):
self.layers = []
def add(self,layer):
self.layers.append(layer)
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
# 마지막 layer(softmax) 의 loss값
def loss(self, t):
return self.layers[-1].loss(t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
if t.ndim !=1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
return np.sum(y==t) / float(x.shape[0])
def forward_pass(self, x):
self.predict(x)
def backward_pass(self, learning_rate):
d_out = 1 # 가장 바깥의 gradient 는 언제나 1이다.
for layer in reversed(self.layers):
d_out = layer.backward(d_out, learning_rate)
def evaluate(self, x_test, t_test):
test_acc = self.accuracy(x_test, t_test)
print("Test accuracy = {0}".format(test_acc))
def train(self, x_train, t_train):
batch_size = 128 # 한 번에 처리할 양 (임의로 데이터를 뽑아 학습시킬 양)
epoches = 20 # back - forward 횟수 (전체 데이터를 도는 횟수)
train_size = x_train.shape[0]
learning_rate = 0.1 # hyper parameter
train_errors = []
train_acc_list = []
iter_per_epoch = int(math.ceil(train_size / batch_size)) # 한 번 돌 때 사이즈
for epoch in range(1, epoches+1):
print("Epoch {0}/{1}".format(epoch, epoches))
for _ in range(iter_per_epoch):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(train_size, batch_size) # 데이터를 랜덤하게 뽑음
x_batch = x_train[batch_mask] # 문제
t_batch = t_train[batch_mask] # 정답
self.forward_pass(x_batch)
loss = self.loss(t_batch)
train_errors.append(loss)
self.backward_pass(learning_rate)
train_acc = self.accuracy(x_train, t_train)
train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
print("Train accuracy={0}".format(train_acc))
return train_errors
def plot_error(self, train_errors):
n = len(train_errors)
training, = plt.plot(range(n), train_errors, label="Training Error")
plt.legend(handles=[training])
plt.title("Error plot")
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.show()
def show_failures(self, x_test, t_test):
y = self.predict(x_test)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
if t_test.ndim !=1 : t_test = np.argmax(t_test, axis=1)
failures = []
for idx in range(x_test.shape[0]) :
if y[idx] != t_test[idx]:
failures.append([x_test[idx], y[idx], t_test[idx]])
for i in range(min(len(failures), 60)):
img, y, _ = failures[i]
if (i%10 ==0 ) : print()
print(y, end=", ")
img = img.reshape(28,28)
plt.subplot(6,10,i+1)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
print()
plt.show()
4. Add Layers to Network
network = Network1()
network.add(Dense(784, 50)) # input layer
network.add(Relu()) # activation function
network.add(Dense(50,10)) # output layer
network.add(SoftmaxWithLoss())hidden layer1개, output layer 1개 를 만들었다.
5. 결과
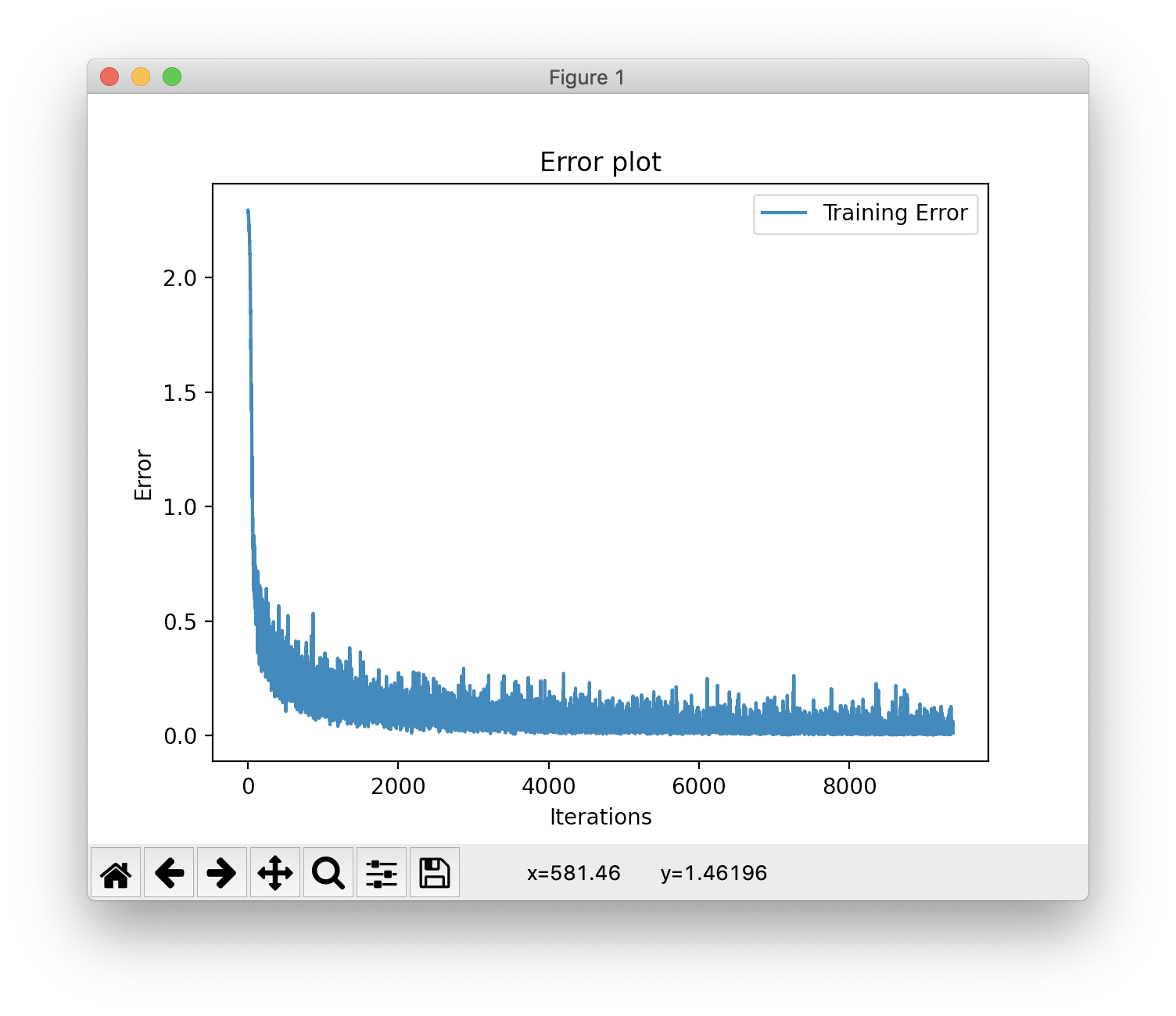
위는 에러율 그래프이다. 시간이 지날수록 점차 낮아짐을 확인할 수 있다.
Epoch 1/20
Train accuracy=0.9028666666666667
Epoch 2/20
Train accuracy=0.92345
Epoch 3/20
Train accuracy=0.9360166666666667
Epoch 4/20
Train accuracy=0.9419833333333333
Epoch 5/20
Train accuracy=0.9462833333333334
Epoch 6/20
Train accuracy=0.95145
Epoch 7/20
Train accuracy=0.955
Epoch 8/20
Train accuracy=0.9594333333333334
Epoch 9/20
Train accuracy=0.9628333333333333
Epoch 10/20
Train accuracy=0.9648
Epoch 11/20
Train accuracy=0.9667833333333333
Epoch 12/20
Train accuracy=0.9689333333333333
Epoch 13/20
Train accuracy=0.9703833333333334
Epoch 14/20
Train accuracy=0.9724833333333334
Epoch 15/20
Train accuracy=0.9733333333333334
Epoch 16/20
Train accuracy=0.9740666666666666
Epoch 17/20
Train accuracy=0.9756333333333334
Epoch 18/20
Train accuracy=0.9764166666666667
Epoch 19/20
Train accuracy=0.9774666666666667
Epoch 20/20
Train accuracy=0.9778166666666667
Test accuracy = 0.9686위는 한 epoch을 돌 때마다 정답률을 프린트 한 것이다. 정답률이 점차 높아짐을 확인할 수 있다.
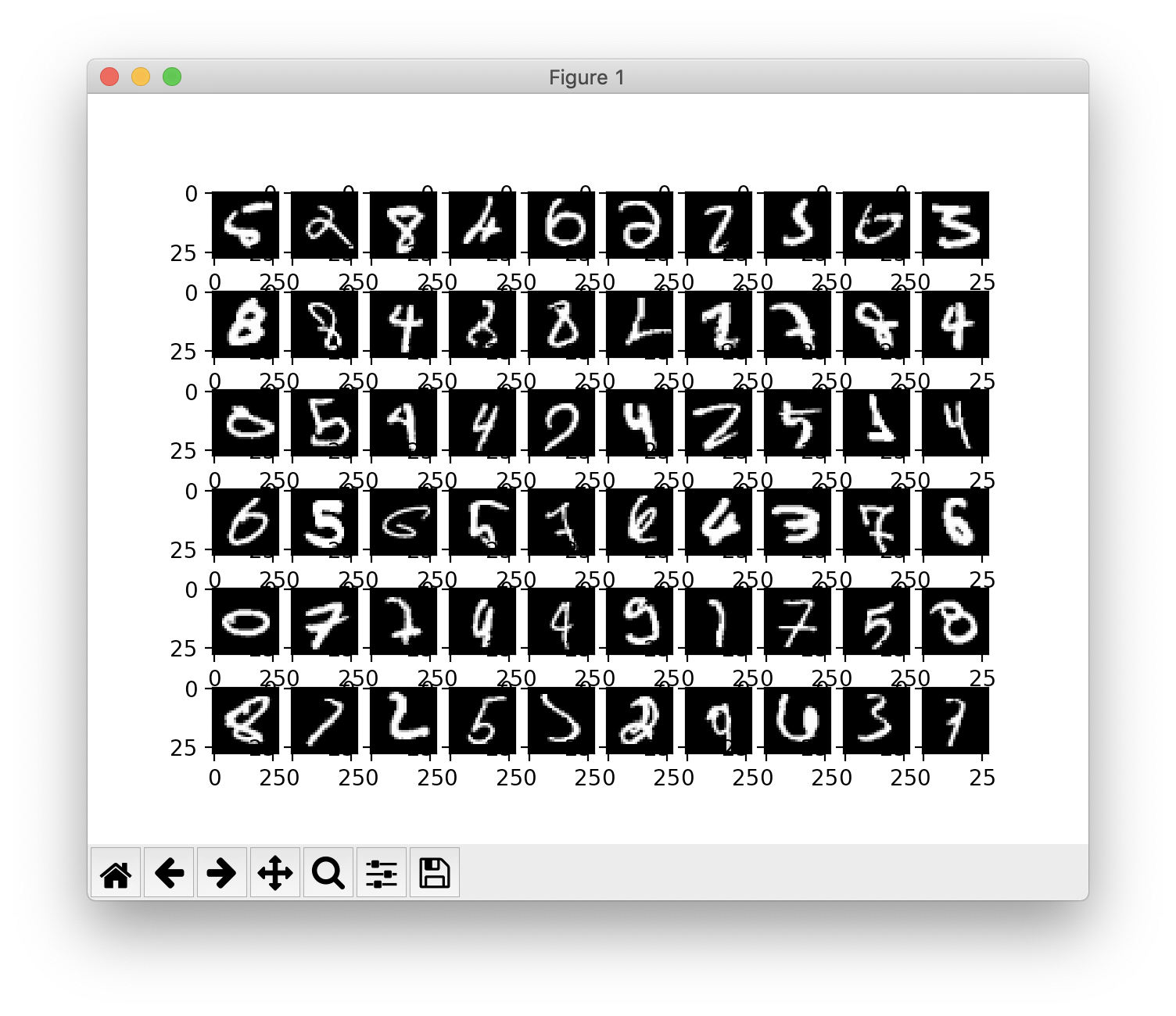
위는 분류에 실패한 예의 이미지를 그린 것이다. (show_failures)




